Manufacturing throughput time: fast-forwarding production
Throughput time breaks down manufacturing processes into bitesize chunks. Make sense of it and produce faster without compromising the quality of your product.

A master production schedule is the backbone of every productive manufacturing business. With this article, you can learn about a master production schedule and how to implement it into your processes.

Here it is — A path to mastery over your day-to-day manufacturing challenges.
It’s called a master production schedule.
It’s an essential supporting document for your entire production planning and scheduling.
In short, it’s a big deal. It’s one of those secret ingredients that takes your business from a good earner to a truly outstanding enterprise. But how can something like a master production schedule do this?
Imagine you’re following a complex recipe from your favorite celebrity chef cookbook.
How would it turn out if the instructions did not give you any information about the amount of each ingredient or the time it takes to prepare and cook? You would spend a long time figuring out how to produce the finished product by looking at videos and pictures. Maybe you’d get it somewhat right, but along the way there would be a lot of thinking time and uncertainty.
This is the difference between having a master production schedule and making do without one.
A small change makes all the difference. That’s why investing time in master scheduling boosts your business’s power and capabilities.
It’s a force multiplier.
In this article, we will look into the master production schedule, its benefits, and the tools you can use to piece your master schedule together.
A master production schedule (MPS) is the overall plan to assess the production of your finished goods, detailing what you need to produce, how much you need to produce, and when you need to produce it.
In short, it contains any relevant information related to production, including time frames, such as your manufacturing lead time. Here is a quick overview of the master production schedule process steps you’ll need to follow when putting this together:
Once you’ve implemented your master schedule, every employee on your shop floor is clear about what needs to be produced each week. Your master production schedule ensures everyone in your business is working towards the same goal. The master scheduler — the MPS architect — can then forecast relationships between demand and supply so you know when to increase or decrease production.
The master production schedule is a crucial input into the aggregate operations plan, giving an overview of everything your business needs to do for 100% order fulfillment.
This is producing sales orders and delivering them on time, without any problems or defects. This is known as a perfect order — which is what every business should strive for on all their sales channels.
The purpose of a master production schedule is to save you time by making the hours you spend managing your production flow much more efficient, giving you more space to scale your manufacturing business. Once you understand this ultimate goal of the master schedule, you can make sure that the other objectives are all aligned toward achieving this goal. Here are the other functions of a master production schedule.
How will you manage operations to balance demand, labor requirements, and equipment capability? MPS in operations management will help you determine how many items you need to produce within a specific period.
A master production schedule should consider multiple manufacturing routes to determine the most efficient and consider any problems that might occur along a production line.
Rough-cut capacity planning with your master production schedule helps you figure out the realistic capacity you need to meet demand, increase profits, and minimize your costs.
The master schedule helps you set your reorder points to make deliveries that need to be placed. You can coordinate different management information systems such as marketing, finance, etc.
Finally, a master production schedule will help you establish the loads and utilization requirements for machines and equipment.
The other master production schedule objectives are:
Those are the desired outcomes of your master schedule. Now let’s look at the ingredients of the ideal master production schedule.

You’ll need a demand plan when you put together your production calendar. You need up-to-date and accurate historical sales data to generate said demand plan. You can use this to determine your projected demand for the upcoming weeks.
Just make sure that you adjust this on a week-to-week basis.
Keeping some safety stock around is good in case you receive an unusually large or uncommon order. If your demand grows, you need to increase your order policy so it does not frequently eat into your safety stock.
So as each week passes, you update your demand plan to create a more accurate production calendar. Your MPS manufacturing may be a work-in-progress, but you will fine-tune it, making it a valuable tool for your business’ order fulfillment.
The correct procedure for developing a master production schedule is to include the following elements:
What benefits can you expect to reap once you implement a master production schedule into your business planning?
Let’s review a master production example for a leather manufacturer selling bags.
To simplify this production schedule example, let’s look at just two products, with two variations each, making four SKUs:
First, let’s see how this looks in a run-of-the-mill master production schedule that thousands of businesses currently use.
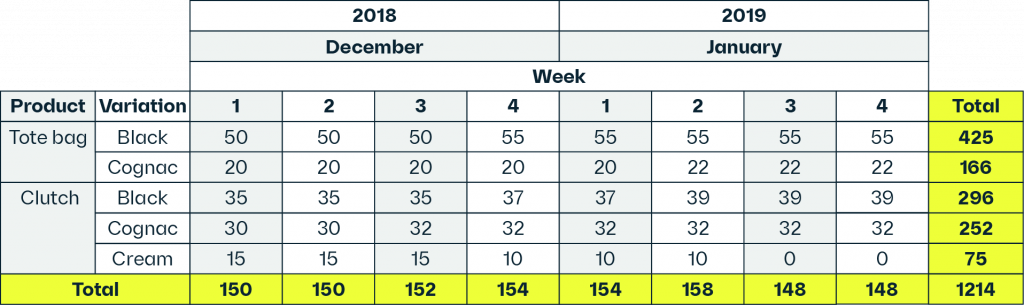
Hard on the eyes, right? Apart from being hard on the eyes, one downside to this approach is that the master production schedule is not dynamic.
It doesn’t change based on actual orders and capacity. You have to update it yourself as it is based on a spreadsheet program. Excel is inefficient and vulnerable to business-harming errors.
That’s why manufacturers, especially scaling ones, turn to tools such as MES software to help them put together a more visually appealing and dynamic master production schedule.
But before we look into a master production schedule being used within a cloud-based manufacturing system, let’s quickly look into the difference between a master production scheduling and production scheduling, both very important steps in manufacturing.
So, what kind of manufacturers use a master production schedule?
Well, no matter the size or type of your manufacturing business, the sooner you start, the better. This is because it fosters good business habits, so things like creating and managing a master schedule become second nature when you finally scale up. Your business habits are a key predictor of long-term success.
The master production schedule is compatible with different production workflows:
Master production scheduling focuses on producing finished goods or components (if you have an ATO workflow).
The most profitable goods for your business will likely make up most of the resources needed for production. Ultimately, manufacturers use their master production schedule to help them:
So, when you’re putting together your master production schedule, you also need to consider these other important variants when utilizing your MPS:
There can be confusion between a master production schedule and a production schedule since the processes to develop the two can be similar.
So, to tell them apart, here is the difference between an MPS and a production schedule:
The continuous optimization process that businesses need to carry out determines the number of finished goods they need to produce based on the inputs and constraints of their production.
On the other hand, production planning is the early stages of your manufacturing process, where you’ll define the production levels with limited and fewer details. Production planning aims to determine the production of items in terms of families or groups.
Now you’re updated on what is a master production schedule and the difference between production planning, you might realize that putting together an MPS is a lot of work.
Fortunately, software on the market can automate this process for you, so you can put together your master production schedule in no time and get right back to growing your business.
Katana is a tool for manufacturers looking to centralize their entire business, from master production planning to manufacturing and even sales.
Katana comes with a master production schedule or real-time master planner, which automates the tasks associated with your master schedule and streamlines the entire process. So, using the earlier example, let’s take another look at a master production schedule in Katana.
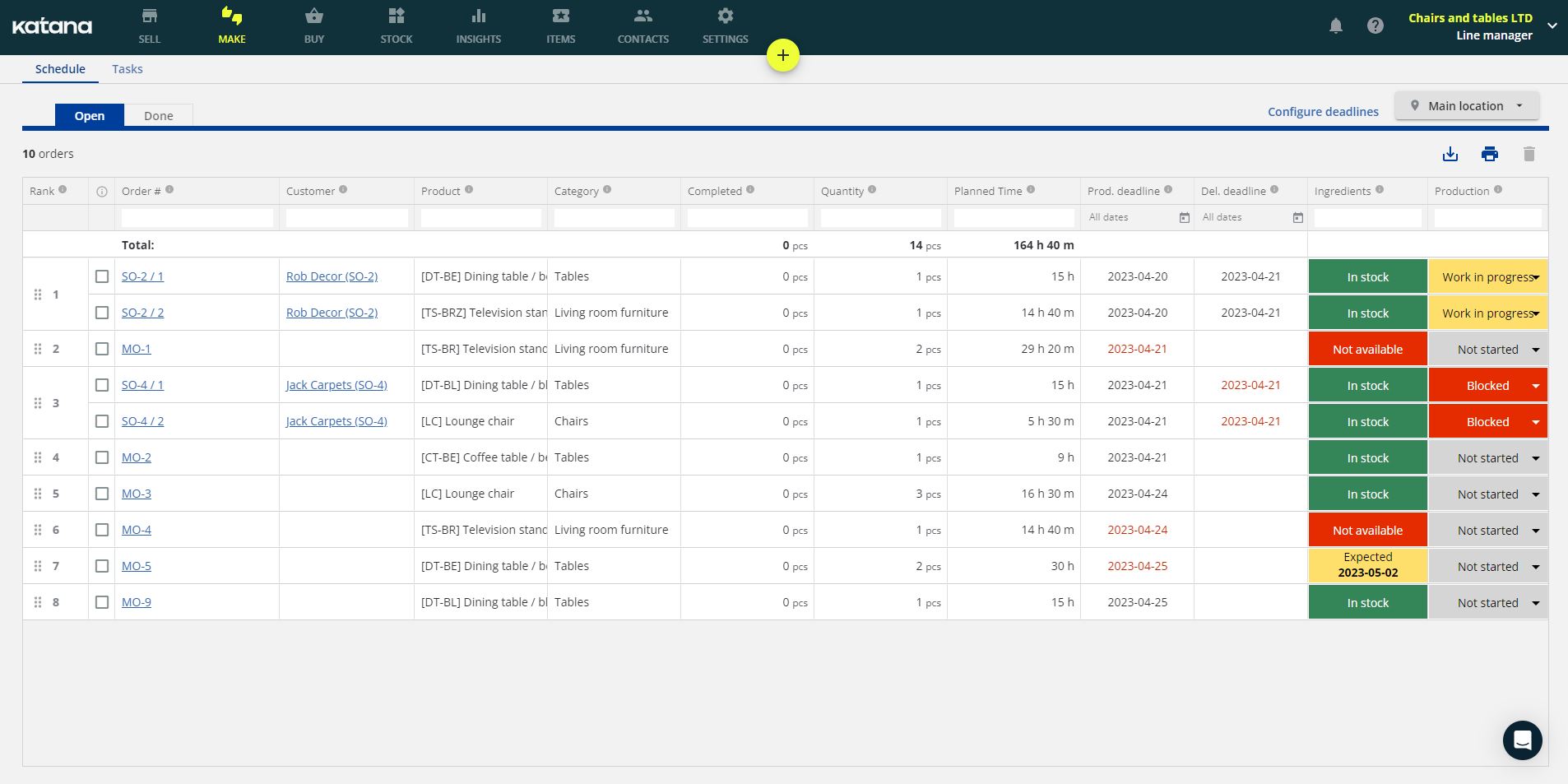
This is the “Make” screen in Katana.
All the information you require from a master production schedule is here – amounts, production time, and deadlines. You can access the bill of materials for any manufacturing order by clicking on the row you want to access. Every staff member also has their own personalized schedule.
Pro tip: Click on “All Dates” below the “Production Deadline” (4th column from the right) to change the date range. You can review your schedule for the current day and the next seven days. In fact, you can set “Custom Dates” to customize your master production schedule as much as you need.
See how subtle changes can make all the difference?
But what about your raw materials planning? Easy. Click on an MO (manufacturing order) field to open up a detailed breakdown of its production schedule.
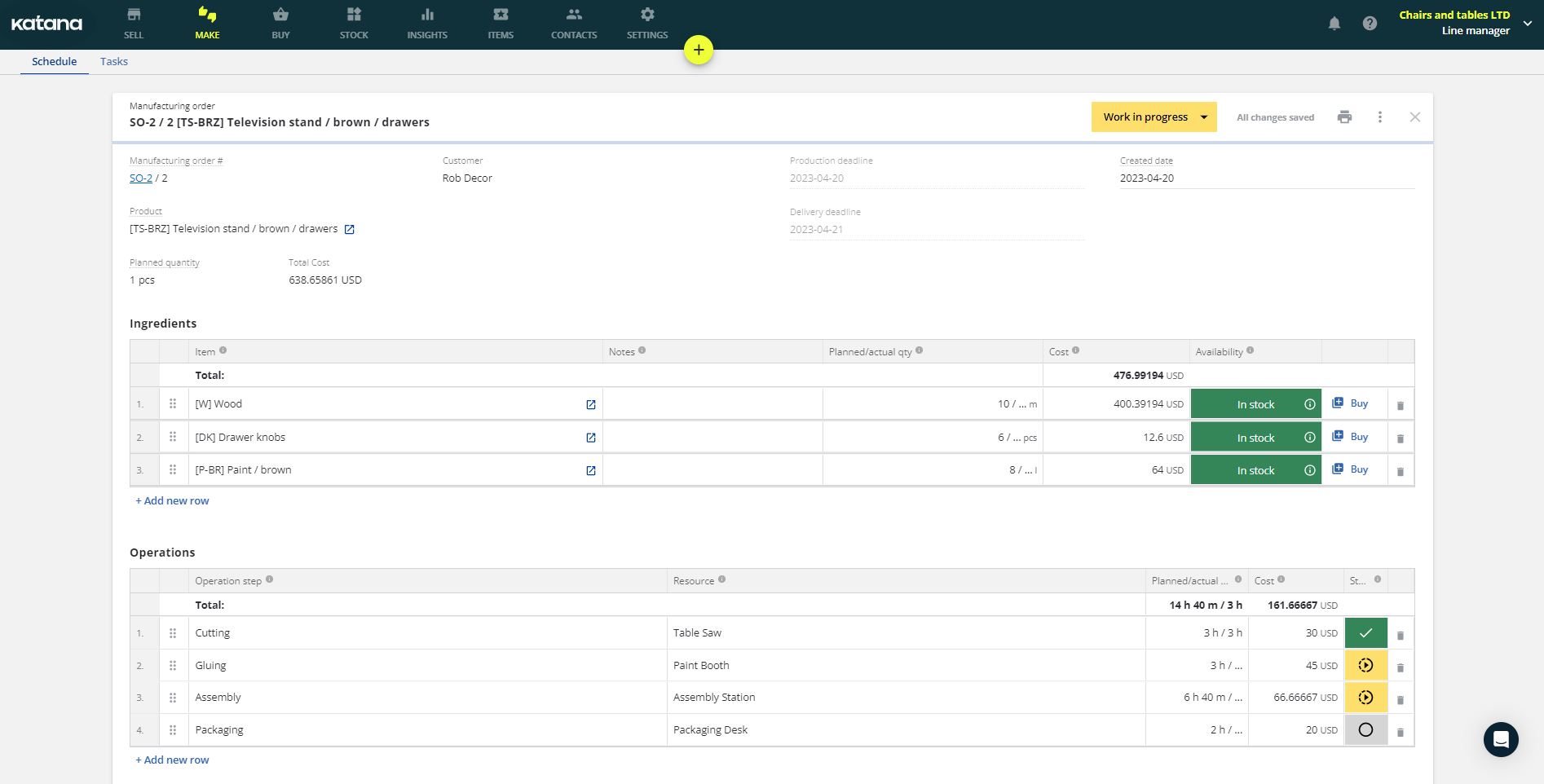
This is the manufacturing order (MO) card in Katana. It is the part of the master production schedule that contains the bill of materials (BOM) and product recipe. It is very useful as it contains all your quantities and process, so you or your staff are never lost for how to produce something.
The product is split up into every part and component, which is given its own deadline for completion.
This advanced tool ensures you never slip up on the details, keeping you on schedule. Finally, you can review your staff members’ schedules. Do this by clicking on “Tasks” in the “Make” screen (the make screen is the central hub for your master production schedule).
The production schedule for each person in your team is laid out clearly.
Everyone has a job to do every minute of every day. You just need to decide when to break for lunch. When no time is wasted or lost, you’ll get your orders done much quicker.
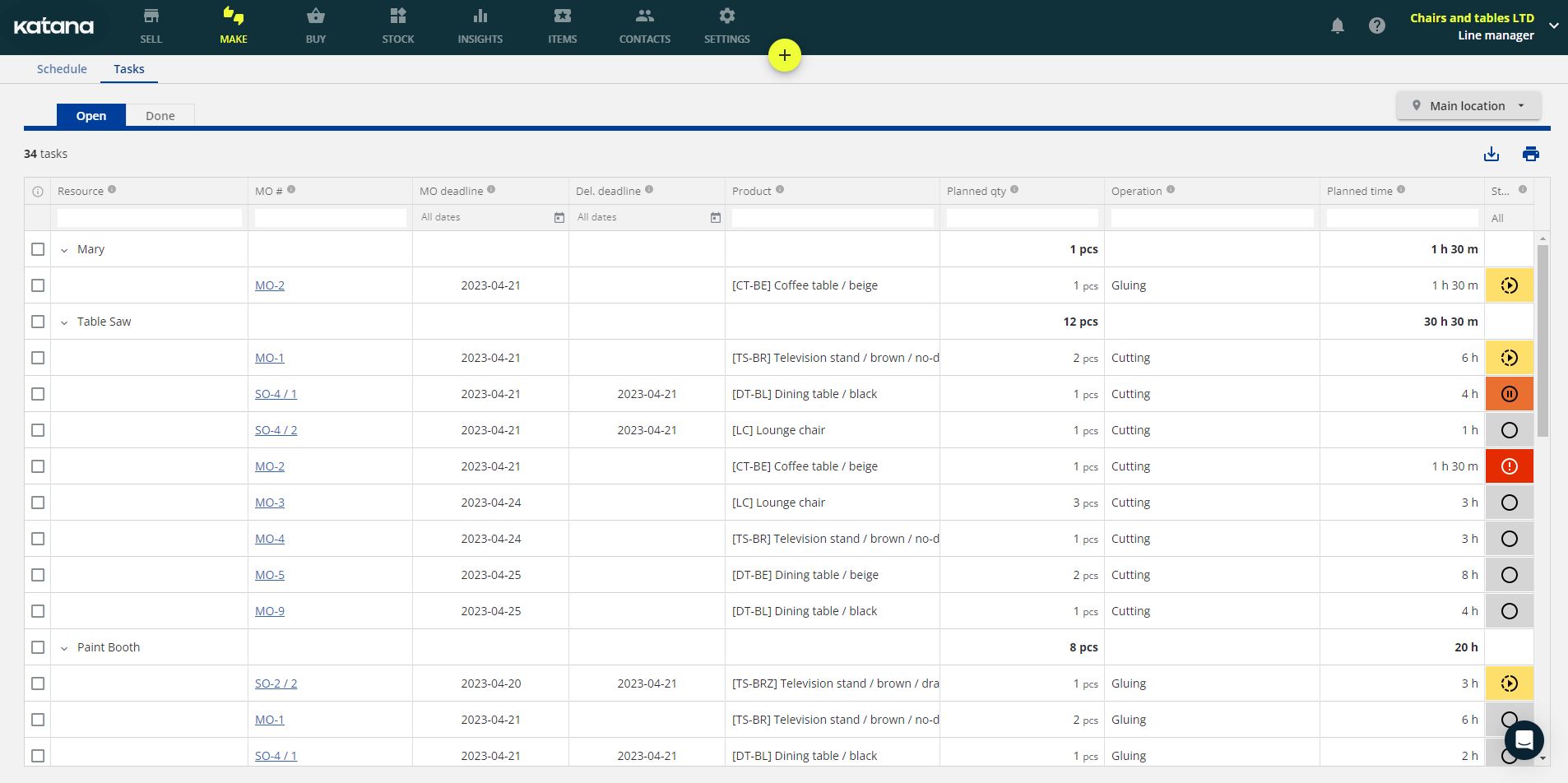
This is the “Tasks” screen in Katana which shows you all the necessary operations for open MOs. You can assign and reassign tasks in a matter of seconds using a drag-and-drop system. All processes and sub-processes are scheduled so you know how long production will take, and hit your deadlines.
Pro tip: Katana gives manufacturers access to the Shop Floor Control App, perfect for managers with multiple employees who need a clear communication channel with their shop floor, available on the Advanced plan.
The trick is to find master production scheduling software that doesn’t make you shudder with dread when you open it. Seriously — the better you feel about your software, the more motivated you will feel to learn it thoroughly, and the more likely you are to use it effectively.
And there, you have everything you need to know about the master production schedule and how you can put yours together.
However, it’s one thing to know, but without using cloud manufacturing software to manage your master production schedule, you’re going to be stuck with a system like using inefficient Excel spreadsheets. This is why manufacturers turn to cloud-based manufacturing software to help them automate the process of making their master production schedule automated and easy to understand. Why not try out an automated master production schedule within your business with a 14-day free trial to see how much it can improve the efficiency of your production lines.
We hope you found this article useful, and if you have any questions, feel free to message us here or over on our social media channels, and until next time, happy manufacturing.
The main functions of an MPS are as follows:
Production planning
The MPS helps plan the production process by providing a detailed schedule of what products will be produced, how much will be produced, and when production will occur.
Resource planning
The MPS helps to ensure that the necessary resources, such as raw materials, labor, and equipment, are available to meet the production schedule.
Inventory control
The MPS helps to control inventory levels by determining the quantity of finished products that should be produced and when they should be produced.
Customer service
The MPS helps improve customer service by ensuring products are produced on time and delivered to customers as promised.
Capacity planning
The MPS helps to plan and optimize the capacity of the production process to ensure that it can meet the demand for products.
Performance evaluation
The MPS provides a basis for evaluating the performance of the production process by comparing actual production against the planned schedule.
Material requirements planning (MRP) and master production schedule (MPS) are two different but related manufacturing planning tools. The main differences between MRP and MPS are:
Scope
MRP is concerned with managing the materials required for production, whereas MPS is concerned with managing the overall production plan.
Time horizon
MRP focuses on the short-term, typically covering the next few weeks or months, while MPS is a longer-term plan, usually covering a period of several months to a year.
Inputs
MRP relies on inputs such as the bill of materials, inventory levels, and customer orders, while MPS relies on inputs such as sales forecasts, production capacity, and inventory policies.
Outputs
The main output of MRP is a list of materials and quantities required for production, while the main output of MPS is a detailed production schedule that outlines what will be produced, how much, and when.
In summary, MRP is a material-focused planning tool that calculates material requirements to meet the production schedule, while MPS is a production-focused planning tool that outlines the production plan and schedules required to meet demand.
The main difference between a master schedule and a production schedule is their level of detail and time horizon.
A master schedule is a high-level plan that outlines the overall production plan for a specified period, typically several months to a year. It provides a general overview of what products will be produced, the quantities to be produced, and when production will occur. The master schedule considers factors such as production capacity, inventory levels, and customer demand to ensure the production plan is realistic and achievable.
On the other hand, a production schedule is a more detailed plan that breaks down the master schedule into specific production units, typically a day or a week. It specifies the quantity of each product to be produced, the start and end dates of production, and the resources required to produce each item. The production schedule considers factors such as machine and labor availability, setup time, and lead time to ensure that the production plan is executed efficiently.
In summary, a master schedule is a high-level plan that provides an overview of the production plan for a specified period. In contrast, a production schedule is a detailed plan that breaks down the master schedule into specific production units, typically a day or a week.