Manufacturing lead time: what it is and how to reduce it
Lead time is the time taken from scheduling to delivering a product. Reducing lead time is vital for your business efficiency. Find out how to reduce lead time.

Production planning and scheduling is essential to increase your manufacturing efficiency. Adjust your production schedule based on inventory, resources, and orders. Learn how with Katana.

Production scheduling is essential for growing manufacturing operations to take their production to the next level. If you’re looking to maximize efficiency on your shop floor, you need a way to optimize your production planning and scheduling.
Nowadays, your scaling manufacturing business has many options for finding production planning software explicitly crafted for manufacturers.
This guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing scheduling and how it can help you allocate your resources efficiently and cost-effectively to meet customer orders. So, read on to learn how to improve production scheduling in your scaling manufacturing business.
Production planning and scheduling are two key activities in manufacturing and operations management. Although closely related, they involve different aspects of the production process. Let’s take a closer look at the difference between these two concepts.
Production planning is an important process that involves strategic decision-making to determine the optimal production strategy, resource allocation, and scheduling to meet customer demand and organizational objectives. It encompasses a comprehensive analysis of what products should be produced, in what quantities, and when.
By considering market demand, sales forecasts, and internal capabilities, production planning ensures efficient utilization of resources while maintaining a competitive edge in the market. This process plays a vital role in aligning the overall business strategy with the operational aspects of production, enabling companies to meet customer expectations, maximize productivity, and achieve their desired outcomes.
The main objectives of production planning include:

Production scheduling is a vital process that entails the creation of a comprehensive and detailed timetable outlining the specific order and timing of production activities. It involves making critical decisions on when each task or operation should commence and conclude, taking into account resource availability, constraints, and dependencies.
By considering factors such as machine availability, labor capacity, and material availability, production scheduling aims to optimize efficiency and streamline workflow.
This process ensures that production tasks are executed in a coordinated manner, minimizing idle time, maximizing resource utilization, and ultimately facilitating the timely delivery of products.
Effective manufacturing scheduling plays a pivotal role in enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and maintaining a smooth and well-organized production process.
The primary objectives of production scheduling include:
In summary, production planning focuses on the big picture and long-term decisions to ensure that production activities align with the overall business strategy and customer demand. On the other hand, production scheduling focuses on short-term decisions that aim to optimize efficiency, minimize costs, and maintain a smooth workflow within the production process.
Both planning and scheduling are essential for effective production management and meeting customer demands efficiently.
Production planning and scheduling are crucial aspects of a business’ operations and have significant importance for several reasons:
So, if you want to ensure timely delivery, optimal resource utilization, cost control, improved efficiency, and scalability, you need to have a solid production plan.

Production planning and scheduling involve a systematic approach to ensure efficient and timely production of goods. The best way to achieve this is by dividing the process into four distinct stages, each serving a specific purpose.
These stages provide a structured framework for organizations to plan, schedule, and control their production processes effectively. Let’s explore each stage in detail.
The first production planning and scheduling stage involves demand forecasting and capacity planning.
Demand forecasting entails estimating future customer demand based on historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors. It helps organizations determine the expected demand volume and patterns for their products.
To forecast demand, you need to incorporate a variety of data, including:
Learning and understanding your product demand will help you make the best choices when arranging and improving your operations.
Once the demand is forecasted, capacity planning comes into play.
It involves evaluating the production capacity and capabilities of the organization to determine if it can meet the projected demand. Factors such as workforce availability, equipment capacity, and facility constraints are taken into account during this stage.
The goal is to align the production capacity with the anticipated demand to avoid underutilization or overburdening of resources.
The second stage focuses on inventory control, including material planning and procurement. In this stage, organizations identify the raw materials, components, and resources required for production. The quantities needed are determined based on the manufacturing schedule and demand forecast.
Efficient material planning ensures the timely availability of materials while minimizing inventory costs and the risk of shortages or excess stock.
Establishing strong supplier relationships is essential during this stage to ensure a reliable supply chain. Organizations collaborate with suppliers to coordinate delivery schedules, negotiate pricing, and maintain consistent quality standards.
Effective material planning and procurement help optimize production flow and prevent disruptions in the supply chain.
The third stage involves detailed scheduling and resource allocation. It focuses on creating a comprehensive production timeline and sequence of activities to ensure smooth operations.
Scheduling involves assigning tasks to different workstations or production lines, considering factors such as equipment availability, setup times, and dependencies between jobs.
Resource allocation is another crucial aspect of this stage. It entails determining the optimal allocation of labor, equipment, and other resources to specific production tasks. Balancing workloads, considering skill levels, and maximizing resource utilization are key considerations during resource allocation.
The goal is to create an efficient schedule that minimizes idle time, bottlenecks, and unnecessary delays.
The fourth stage revolves around production control and monitoring. Once production is underway, it is essential to track work progress, ensure adherence to the planned schedule, and maintain quality standards. Production control is all about monitoring the production process, identifying deviations or bottlenecks, and taking corrective actions as necessary.
Efficient production control relies on real-time data collection, performance measurement, and analysis. It enables organizations to identify issues, make adjustments, and optimize the production flow. This stage also includes quality control measures to ensure the final output meets the required standards and customer expectations.
Once your manufacturing plan looks achievable, you can progress to the next step, producing a master production schedule, the ultimate document for production.
Your master production schedule (MPS) will detail how many items need to be produced within a certain period. Most manufacturers use manufacturing technology to create an MPS that will provide real-time data and allow manufacturers to make production changes on the fly.
By effectively controlling and monitoring the production process, organizations can improve productivity, minimize waste, and ensure timely delivery of products to customers.
Imagine a small but modest workshop with five artisans making psychedelic T-shirts.
Each artisan works eight hours a day, from Monday to Friday. They follow a make-to-stock workflow in a job shop setting. It takes 2 hours to produce a single T-shirt.
The max capacity of this Funkadelic business is 200 hours.
In this scenario, the annual hippie fest is fast approaching — and looking at your historical data collection — the T-shirt makers expect to see a surge in sales. Last year they were overwhelmed, so this year, they have decided to put together a quick manufacturing plan a week before they expect an increase in demand. They also want to have a safety stock level of ten for each of their items.
As per their initial plan, they won’t be able to meet production requirements, but they can now use this knowledge to readjust their current production plan. They decide to limit the production of Far Out T-shirts to 40 and Peace T-shirts to 8.
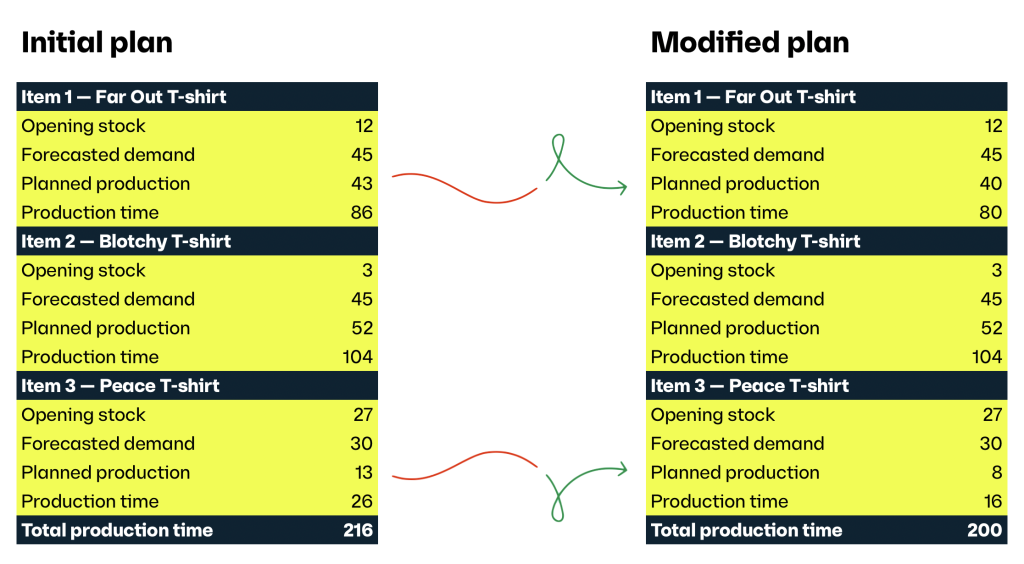
They can still meet the forecasted demand with the modified plan by sacrificing some of the safety stock.
However, this plan put their operations and resources at 100% capacity. If one of the artisans calls in sick on Wednesday evening, the max capacity for the week falls to 176 hours. When planning production, a rule of thumb is to have 20% free to give yourself wiggle room if a problem occurs.
Production planning is vital for any manufacturing business. Even basic products need a clear and defined flow to turn them from raw materials into quality goods. If you don’t follow this flow or your production quality control checklist, your products will surely drop in quality. Without a proper process, your standardized practices will be forgotten.
So, when scheduling the production, what are the key factors to consider?
Use your team well.
Your people are a valuable asset to your business. They play a key part in manufacturing process optimization. Make it your business to know your people, including their strengths and weaknesses. This way, you can assign each team member to the most suitable tasks and machines.
If someone is sick or goes on holiday, you have the additional capacity to make up for the temporary loss.
Effective production planning allows you to get the most out of your people and machines. Every team member knows the tasks assigned to them and what their expected output is. Keeping tabs on this process lets you compensate for shortfalls and keep up with high demand.
Is your workshop constantly running at 100% of its output?
It only takes a minor bump to bring things to a grinding halt. Capacity planning helps to make sure you’re not running at max capacity. If you do receive an unusually large order or two, you will be glad you prepared.
The same goes for your team, as they have enough resources to do their job on time.
Frequent stalls in production planning mean paying team members and machines to stand by.
Integrating a robust MRP or manufacturing ERP software into your business can help ensure you always have the required raw materials available. This means:
If done right, warehousing and transport costs won’t skyrocket due to oversupply. As a bonus, every team member always has something to do as they work with your available materials.
The logistical flow of each part of your manufacturing process also requires consideration. This may not seem so important, but you would be surprised. Many production lines have come grinding to a halt as one weak link has been placed on the wrong stage.
Pushing machines and people to unsuitable locations can harm efficiency.
Sometimes, what seems like common sense could be harmful to your flow. It takes careful analysis to determine how materials, resources, people, and supplies travel around your shop floor.
It may be that a more efficient layout or order exists for your business. Sometimes a small change can make a world of difference to your production schedule.
Trial-and-error problem-solving costs your business money through each failed attempt.
Overordering or overproducing is a band-aid solution, as this leads to extra costs or staff burnout. You need effective production planning software to track your flow and find manufacturing scheduling issues to get to the root of a problem.
Understanding manufacturing planning and scheduling allow you to oversee your manufacturing methodically to overcome production issues easily.
Track and manage everything effectively, and everything should run like clockwork. Effective manufacturing scheduling makes it easier to do everything by the book — it is set out clearly for your whole team and is available 24/7.

Now you know everything there is to know about putting together your production plan — the next step is understanding how to measure its effectiveness. Here are some KPIs to track to get you started:
This checklist will guide you in creating your business analytics to observe your production and develop plans to make them even more efficient.
But, as you can tell, doing this is a long and arduous process, and many scaling manufacturers turn to automation to help them with this task.
Optimizing production scheduling involves maximizing efficiency, minimizing costs, and ensuring timely delivery of products. Below you’ll find some strategies for optimizing manufacturing scheduling.
Incorporate demand-driven scheduling by aligning manufacturing schedules with customer demand. Use accurate demand forecasting to determine the required production volume and adjust schedules accordingly. This approach helps avoid overproduction or underproduction and reduces excess inventory or stockouts.
Employ advanced scheduling techniques such as finite capacity scheduling, just-in-time (JIT) scheduling, or theory of constraints (TOC) to optimize production schedules. These techniques consider capacity constraints, setup times, and dependencies between tasks to create efficient and realistic schedules.
Ensure optimal utilization of resources by assigning tasks based on skill levels, availability, and efficiency. Consider the capabilities and capacities of equipment, machinery, and workforce while allocating resources. Efficient resource allocation minimizes idle time, reduces bottlenecks, and improves overall productivity.
Reduce changeover and setup times by implementing strategies like single-minute exchange of die (SMED). Streamlining changeover processes allows faster transitions between different product configurations, enabling shorter production runs and increased flexibility.
Utilize real-time monitoring systems and production control tools to track progress, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions. Real-time data provides insights into the actual status of production, enabling prompt adjustments and proactive problem-solving.
Identify critical tasks or processes that significantly impact the overall production timeline. Prioritize these and allocate resources accordingly to ensure timely completion. Focusing on critical tasks minimizes the risk of delays in the entire production process.
Take into account any constraints that may affect production scheduling, such as limited capacity, equipment maintenance schedules, or supplier lead times. By incorporating these constraints into the scheduling process, you can avoid scheduling conflicts and optimize production flow.
Apply lean manufacturing principles such as just-in-time production, continuous flow, and waste reduction techniques to optimize production scheduling. Eliminate non-value-added activities, reduce inventory, and optimize process flows to improve overall efficiency.
Utilize production scheduling software or manufacturing execution systems (MES) with advanced planning and scheduling capabilities. These tools automate the scheduling process, optimize resource allocation, and provide real-time visibility into production activities, enabling better decision-making and scheduling optimization.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and analyzing production schedules, performance metrics, and feedback. Identify areas for improvement, implement changes, and monitor the impact of these adjustments. Continuously striving for optimization ensures ongoing efficiency gains in production scheduling.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can optimize their production scheduling processes, enhance operational efficiency, minimize costs, and deliver products on time, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and competitiveness.

Production planning and scheduling mistakes can lead to inefficiencies, delays, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction. Let’s review some common mistakes to avoid in manufacturing planning and scheduling.
Failing to accurately forecast customer demand can result in overproduction or underproduction. Overproduction leads to excess inventory and increased carrying costs, while underproduction can result in stockouts and missed sales opportunities. It is important to gather and analyze relevant data, consider market trends, and collaborate with sales and marketing teams to improve demand forecasting accuracy.
Inadequate evaluation of production capacity can lead to resource constraints and bottlenecks. If the production capacity does not align with the forecasted demand, it can result in missed deadlines, backlogs, and delays in fulfilling customer orders. Conducting regular capacity assessments and considering factors such as equipment maintenance, workforce availability, and facility constraints are essential for effective manufacturing capacity planning.
Inaccurate material planning can cause disruptions in the production process. Insufficient stock of raw materials or components can halt production, while excessive inventory ties up capital and increases storage costs. Utilizing efficient inventory management systems, establishing reliable supplier relationships, and continuously monitoring material requirements are crucial to avoid material planning errors.
Inefficient scheduling can lead to production issues, increased setup times, and idle resources. Poor task sequencing, inadequate consideration of setup times, and neglecting resource availability can result in unnecessary delays and production bottlenecks. Utilizing advanced scheduling techniques, considering the dependencies between tasks, and optimizing resource allocation is vital for efficient scheduling.
Failure to incorporate flexibility in manufacturing planning and scheduling can make it challenging to adapt to unforeseen events or changes in demand. Market fluctuations, machine breakdowns, and supplier delays can disrupt the planned schedule. It is important to build contingency plans, have backup suppliers, and maintain buffer capacity to accommodate unexpected disruptions and maintain operational continuity.
Neglecting to gather feedback from the production floor, customer feedback, and performance metrics can hinder process improvement.
Regularly reviewing production performance, analyzing data, and actively seeking feedback from relevant stakeholders can help identify areas for improvement and drive continuous optimization in production planning and scheduling.
Poor communication and collaboration among departments can lead to misalignment and delays. Production planning and scheduling require coordination among different teams, including sales, operations, procurement, and logistics.
Clear communication channels, regular cross-functional meetings, and shared visibility of information are essential for effective collaboration and synchronization of activities.
By avoiding these common production planning and scheduling mistakes and adopting best practices, organizations can enhance their operational efficiency, minimize costs, and improve customer satisfaction by consistently delivering products on time and as per requirements.

The absence of affordable production planning software has led to many manufacturers using inefficient spreadsheets.
There are three main problems with this approach:
Many modern manufacturers are stuck with Excel because they can’t see better options.
This is understandable. Most manufacturers do not need the gargantuan flow diagrams and Gantt charts seen in large enterprise software. Shop-bought software like Excel seems like a quick and easy option.
But it is not powerful enough for using production management effectively.
The best way to avoid production planning mistakes and implement different optimization techniques is through software. Katana is a cloud manufacturing platform that allows you to do all that and more. It offers advanced features with an intuitive interface, so you don’t need a 3-month boot camp to start using it.
Let’s have a look at what production planning with Katana looks like.
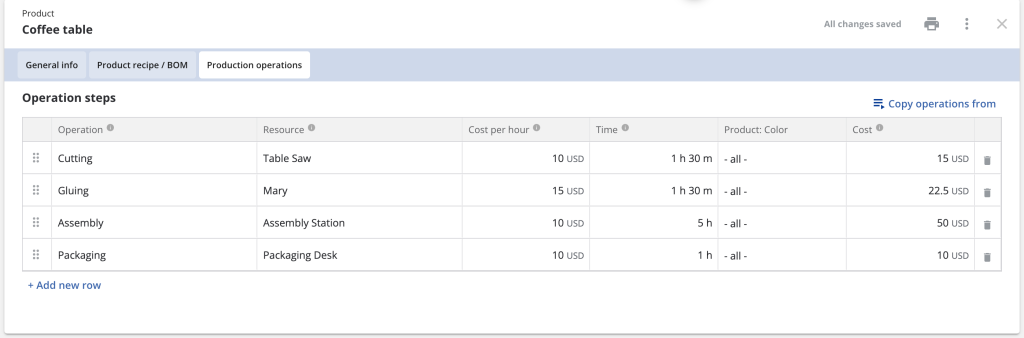
The Production operations tab lets you do production planning as it automatically assigns team members and workstations to each process your manufacturing orders require. It also calculates all the resources needed and associated costs.
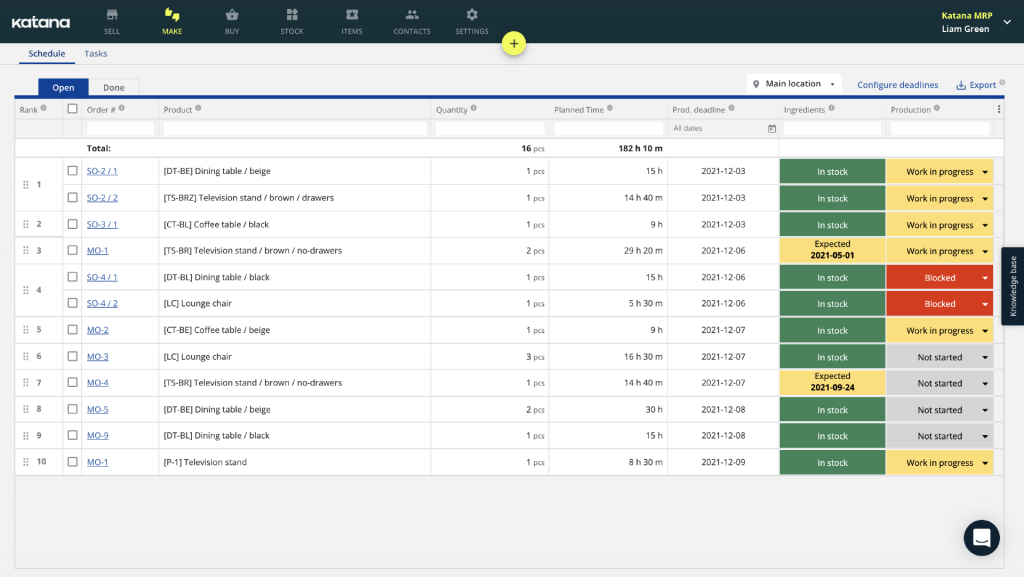
The Make screen lets you review all outstanding manufacturing tasks. If something comes up, or you want to change tack, simply reorganize your manufacturing queue, and Katana’s real-time master planner reallocates all resources to ensure the prioritized orders get out of the door first.
Production planning with Katana allows you to:
Take control of your production processes with Katana. Sign up for a 14-day free trial and see how it can streamline your business.